The powerful and easy to use Chatie DevOps Toolset:
- @chatie/tsconfig: Enables other module to inheritance tsconfig.json via Node.js packages
- @chatie/eslint-config: ESLint Sharable Rules in TypeScript Standard Style
- @chatie/semver: The Enhanced Semantic Versioner for NPM
- @chatie/git-scripts: Git Hooks Integration for Chatie Projects
- tstest: A pytest in TypeScript
- pkg-jq: Find the nearest package.json then deal with jq syntax on it. (in-line edit supported!)
DevOps is king. Chatie dependents DevOps for years and it works great. We have dozens of projects with repositories hosted on GitHub, and publish them to NPM right after a commit & push, through the DevOps pipeline, which mainly under the control of Travis CI.
We had build lots of helper scripts to do those tasks automatically, and today, we had published most of them to NPM modules, so that we will no longer need to copy them everywhere, and we can use NPM version to manage them very well.
So, I’d like to introduce them to the community, and also it’s a quick sheet to check.
1. @chatie/tsconfig

This module enables other module to inheritance tsconfig.json via Node.js packages.
All you need is to:
npm install @chatie/tsconfig
Then it will create a very nice tsconfig.json at the root of project for you, and you will also get the latest TypeScript & ts-node binarys installed.
{
"extends": "@chatie/tsconfig",
"compilerOptions": {
"outDir": "dist",
},
"exclude": [
"node_modules/",
"dist/",
"tests/fixtures/",
],
"include": [
"app/**/*.ts",
"bin/*.ts",
"bot/**/*.ts",
"examples/**/*.ts",
"scripts/**/*.ts",
"src/**/*.ts",
"tests/**/*.spec.ts",
],
}
After extends from @chatie/tsconfig from your tsconfig.json, you will have the chatie version of the TypeScript Configuration, it aim the following goals:
- Support the latest esnext ECMAScript
- Targeting for ES6
- Strict for everything
- Aiming for Convenience, including the esModuleInterop and resolveJsonModule etc.
2. @chatie/eslint-config

ESLint Sharable Rules in TypeScript Standard Style.
npm install --save-dev @chatie/eslint-config
Then it will create a very nice .eslintrc.js for you automatically (if there’s no such file before). It will contains the following content:
module.exports = {
extends: '@chatie',
}
Then you are all set. ./node_modules/.bin/eslint will work and follow the @chatie rules.
3. @chatie/git-scripts

Git Hooks Integration for Chatie Projects.
This module is a wrapper of the NPM module git-scripts, it provide following additional features:
- pre-push hook had been set to run npm run lint and then npm verion patch for better code quality and version management.
By adding the following json entrance to package.json:
"git": {
"scripts": {
"pre-push": "npx git-scripts-pre-push"
}
}
4. @chatie/semver
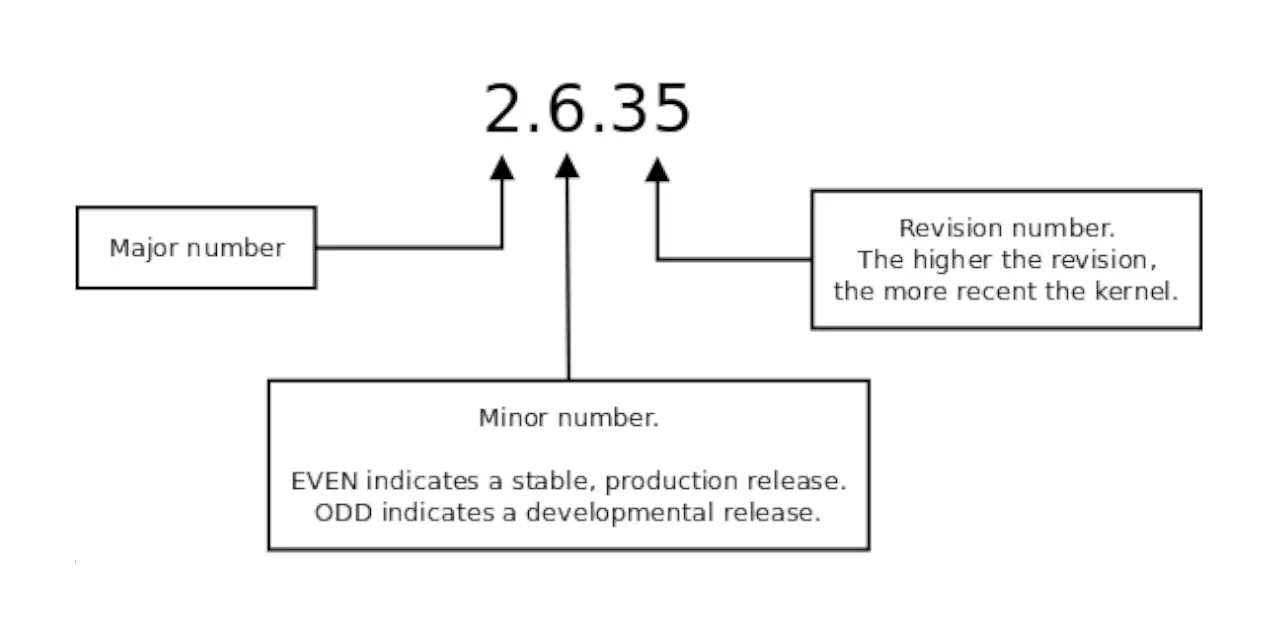
The Enhanced Semantic Versioner for NPM.
This module is a wrapper of the NPM module semver, it provide cli utility for identifying whether the VERSION is for production(stable).
$ semver-is-prod 1.0.0
YES: 1.0.0 is production release
$ echo $?
0
$ semver-is-prod 1.1.0
NO: 1.1.0 is development release
$ echo $?
1
Background
Copy from Linux Kernel Version Numbering - http://www.linfo.org/kernel_version_numbering.html:
The second number denotes the major revision of the kernel version. It was formerly the case that even numbers indicated a stable release, that is, one that was deemed fit for production use (i.e., use in a non-experimental environment), such as 1.2, 2.4 or 2.6. Likewise, odd numbers, such as 1.1 or 2.5, have historically represented development releases. They were for testing new features and device drivers until they became sufficiently stable to be included in a stable release. However, this has changed starting with the Linux 2.6.x series, and new feature development now takes place in the same revision number.
Following the Semantic Versioning 2.0 http://semver.org/, and we will be able to use the MINOR version to indicated the release is STABLE or NOT.
Numbering rule:
- even numbers, such as 0.8, 0.12 indicated a stable release, which is fit for production use.
- odd numbers, such as 0.11 or 0.13, represented as development releases.
See also: https://github.com/wechaty/wechaty/issues/905
5. tstest

A pytest in TypeScript
This module is planed to be a TypeScript version of pytest
However, currently, it’s only a wrapper of blue-tape and @types/blue-tape
6. pkg-jq
Find the nearest package.json then deal with jq syntax on it. (in-line edit supported!)
Features
- Search
package.jsonin current and all parent directories by default, powered by pkg-up. - Use
jqsyntax to deal with the json file, powered by node-jq. In-placeedit support by specify a-ior--in-placeargument.
Example
1. generate-version.sh
This helper script will automatically generate a src/version.ts with the version number from the package.json file of the current project.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -e
SRC_VERSION_TS_FILE='src/version.ts'
[ -f ${SRC_VERSION_TS_FILE} ] || {
echo ${SRC_VERSION_TS_FILE}" not found"
exit 1
}
VERSION=$(npx pkg-jq -r .version)
cat <<_SRC_ > ${SRC_VERSION_TS_FILE}
/**
* This file was auto generated from scripts/generate-version.sh
*/
export const VERSION: string = '${VERSION}'
_SRC_
2. package-publish-config-tag.sh
This helper script will set the NPM module version to @next if the semver is not production, and set to @latest if the semver is production.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -e
VERSION=$(npx pkg-jq -r .version)
if npx --package @chatie/semver semver-is-prod $VERSION; then
npx pkg-jq -i '.publishConfig.tag="latest"'
echo "production release: publicConfig.tag set to latest."
else
npx pkg-jq -i '.publishConfig.tag="next"'
echo 'development release: publicConfig.tag set to next.'
fi
3. Scripts for Installing Chatie DevOps Toolsets for Existing Project
# package.json jq modification util
npm install --save-dev pkg-jq
#
# @chatie/tsconfig
#
# @chatie/tsconfig will re-generate it automatically
rm -f tsconfig.json
npm uninstall \
@types/node \
ts-node \
typescript \
npm install --save-dev @chatie/tsconfig
#
# @chatie/eslint-config
#
# @chatie/eslint-config will re-generate it automatically
rm -f .eslintrc.*
npm uninstall \
@wwwouter/tslint-contrib \
eslint \
markdownlint-cli \
tslint \
tslint-config-standard \
tslint-eslint-rules \
tslint-jsdoc-rules \
npm install --save-dev @chatie/eslint-config
npx pkg-jq -i ".scripts.\"lint:es\"=\"eslint --ignore-pattern tests/fixtures/ '{bin,examples,scripts,src,tests}/**/*.ts'\""
#
# @chatie/git-scripts
#
npm uninstall git-scripts
npx pkg-jq -i 'del(.git)'
npm install --save-dev @chatie/git-scripts
#
# @chatie/semver
#
npm uninstall \
@types/semver \
semver \
npm install --save-dev @chatie/semver
#
# tstest
#
npm uninstall \
@types/blue-tape \
@types/sinon \
blue-tape \
sinon \
sinon-test \
npm install --save-dev \
tstest \
#
# Other Settings
#
# Set default npm publish tag to @next instead of @latest
npx pkg-jq -i '.publishConfig.tag="next"'
Author: huan, A DevOps fan.

 居然有人能忘记吃饭?写个微信机器人提醒他
居然有人能忘记吃饭?写个微信机器人提醒他