一个支持Wechaty调用的Python框架
特征:
- 你可以只会python
- 支持Wechaty全部协议,全部接口
- 兼容同步/异步编程
- 可拓展至其他app/社交平台
声明:作者是更加支持native的python-wechaty的哈,看好@Huan和@wj-Mcat的工作! 不过貌似开发还需要一段时间,有需要的童鞋可以暂时用MetaPuppetForPython。
Talk is cheap, show me the code
初级:Hello Human
目标:更改微信签名 要点:你可以调用类似
a_server.change_self_signature()的函数来主动调用Wechaty的各种接口,从而主动查找联系人,发信息等。 你可以在SocketServerCore和SweetSocketServer中找到更多类似的函数。 但他们其实都是只语法糖(下文会介绍原理),你也可以继承SweetSocketServer,然后根据自己的需要设计自己的函数。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import time
from MetaPuppet.core.SweetSocketServer import SweetSocketServer
from MetaPuppet.core.TestBot import TestBot
if __name__ == '__main__':
# init
a_bot = TestBot(name='test')
a_server = SweetSocketServer(
robot=a_bot,
num_async_threads=1,
debug_mode=True
)
a_server.run()
print(
'Please make sure the client is connected '
'before run the following codes'
)
time.sleep(20)
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
a_server.change_self_signature('Hello Human!')
初级:a simple bot
目标:一个简易机器人。自动接受加人邀请,并问好
Hello Human!。自动回复,内容为接收到信息的反序。 要点:你可以继承RobotBase然后override_process_message()和_process_friend_invitation()函数。 这些函数在收到相关微信信息后会被自动调用,你可以把机器人自动回复的逻辑放在这个类中。 通过这种方式,你可以处理所有的被动请求。结合Hello Human!的例子,你可以主动发出请求。 到此,你已经可以实现全部的业务逻辑。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import time
from MetaPuppet.core.SweetSocketServer import SweetSocketServer
from MetaPuppet.core.RobotBase import RobotBase
class MyBot(RobotBase):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
async def _process_message(self, message, verbose=False):
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
return_msg = None
if 'payload' in message and 'text' in message['payload']:
return_msg = message['payload']['text'][::-1]
return return_msg
async def _process_friend_invitation(self, message, verbose=False):
return_msg = {
'wx_msg_type': 'TEXT',
'path': 'Hello Human!',
}
return return_msg
if __name__ == '__main__':
# init
a_bot = MyBot(name='test')
a_server = SweetSocketServer(
robot=a_bot,
num_async_threads=1,
debug_mode=True
)
a_server.run()
print(
'Please make sure the client is connected '
'before run the following codes'
)
time.sleep(20)
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
# nothing needed here in this example
# however, you can put your other backend code here
中级:语法糖
目标:自定义函数:发送文本给特定联系人/群聊 要点:MetaPuppetForPython实际上是用python将ts的代码片段转发给node并编译运行(详见原理部分),所以若已有的语法糖不能满足需求,你需要定义自己的函数。 由于ts的代码和python其实比较相似,并且往往只需要写很少的ts的代码,主要业务代码还是python,所以自定义函数的难度应该不大。 你可以继承
SweetSocketServer,然后在自定义函数中调用exec_wx_function()或exec_one_wx_function()执行文本格式的ts代码。 如果你需要使用第三方的ts库,可以在socket_client/src的相关代码中声明。
同步代码的语法糖:
from MetaPuppet.core.SweetSocketServer import SweetSocketServer
class ExtendedSocketServer(SweetSocketServer):
# definition for other functions/variables
...
def send_wx_msg_text(self, text, username, chat_type):
ts_code = '''
let say_content = `{}`
const a_contact = bot.{}.load('{}')
await a_contact.say(say_content)
'''.format(text, self.all_chat_type[chat_type.lower()], username)
self.exec_wx_function(
ts_code=ts_code,
need_return=False,
)
异步代码的语法糖(只需要在函数的定义前加上async,在调用异步函数前面加上await):
from MetaPuppet.core.SweetSocketServer import SweetSocketServer
class ExtendedSocketServer(SweetSocketServer):
# definition for other functions/variables
...
async def async_send_wx_msg_text(self, text, username, chat_type):
ts_code = '''
let say_content = `{}`
const a_contact = bot.{}.load('{}')
await a_contact.say(say_content)
'''.format(text, self.all_chat_type[chat_type.lower()], username)
await self.async_exec_wx_function(
ts_code=ts_code,
need_return=False,
)
中级:同步/异步
目标:通过使用异步编程加速代码 要点:同步和异步的区别是在等待响应时前者是真的等待,后者是会缓存当前程序,执行其他异步程序,收到响应时恢复当前程序继续执行。 需要等待的情况有:网络通信等待回复,等待其他某个进程结束,人为使用等待/睡眠等函数。 所以,对于大多数看到这篇帖子的人而言,异步代码加速的主要是网络通信的部分。 如果同步代码本身很慢,将其改为异步并不能减少其执行时间。 基于MetaPuppetForPython的原理,对于频繁调用Wechaty的函数,建议使用异步编程,如默认的
_process_message()就是异步函数。 在_process_message()中,若需要经常调用Wechaty函数,建议使用异步版本的语法糖;若仅是偶尔调用,使用同步版本亦可。 当然,为避免所有函数都需要异步定义,建议在设计层面将Wechaty的相关调用放在比较上层的位置,甚至与核心的同步代码相互独立。 对于大部分业务代码,只是偶尔调用Wechaty函数,可以直接使用同步风格的语法糖,并不影响效率。
异步:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import threading
import time
from MetaPuppet.core.SweetSocketServer import SweetSocketServer
from MetaPuppet.core.RobotBase import RobotBase
from MetaPuppet.core.time_classes import Time
from MetaPuppet.core.utils import run_coroutine_in_new_thread
class MyBot(RobotBase):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
async def _process_message(self, message, verbose=False):
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
return_msg = None
if 'payload' in message and 'text' in message['payload']:
return_msg = message['payload']['text'][::-1]
return return_msg
async def _process_friend_invitation(self, message, verbose=False):
return_msg = {
'wx_msg_type': 'TEXT',
'path': 'Hello Human!',
}
return return_msg
async def async_foo(server):
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
rooms = await server.async_exec_one_wx_function(
func_name='bot.Room.findAll',
func_paras=[],
need_return=True,
)
print('Time:', Time())
print('async_foo', threading.currentThread().getName())
if rooms is not None:
print('async: len(rooms)', len(rooms))
print(rooms[0])
else:
print('async: rooms not found')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# init
a_bot = MyBot(name='test')
a_server = SweetSocketServer(
robot=a_bot,
num_async_threads=1,
debug_mode=True
)
a_server.run()
print(
'Please make sure the client is connected '
'before run the following codes'
)
time.sleep(20)
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
# async version
# better to use async version because sync version might block io
run_coroutine_in_new_thread(
async_foo(a_server)
)
同步:
...
def bar(server):
contacts = server.exec_one_wx_function(
func_name='bot.Contact.findAll',
func_paras=[],
need_return=True,
)
print('Time:', Time())
print('bar', threading.currentThread().getName())
if contacts is not None:
print('sync: len(contacts)', len(contacts))
print(contacts[0])
else:
print('sync: contacts not found')
if __name__ == '__main__':
...
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
# sync version
# sync code is simpler, though not recommended for heavy load
# you can use it if you don't need to use many async functions
# (e.g. async_exec_one_wx_function) at the same time and also
# (1) the task here is short-term and light-load
# or (2) you have a powerful computer
bar(a_server)
中级:线程
目标:通过使用多线程加速代码 要点:上文中提到,异步主要是提升io方面的效率。 对于需要较长计算时间的代码本身,异步帮助不大。 此时可以使用多线程来避免堵塞其他任务。
SweetSocketServer会默认开放一个线程进行消息的自动回复,需要的情况下可以设置初始化参数num_async_threads增加线程数。
...
def bar(server):
contacts = server.exec_one_wx_function(
func_name='bot.Contact.findAll',
func_paras=[],
need_return=True,
)
print('Time:', Time())
print('bar', threading.currentThread().getName())
if contacts is not None:
print('sync: len(contacts)', len(contacts))
print(contacts[0])
else:
print('sync: contacts not found')
if __name__ == '__main__':
...
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
# sync version
# sync code is simpler, though not recommended for heavy load
# you can use it if you don't need to use many async functions
# (e.g. async_exec_one_wx_function) at the same time and also
# (1) the task here is short-term and light-load
# or (2) you have a powerful computer
# however, pay attention that you should run the task here in a new thread
# it is not good to run it in the main thread
threading.Thread(
target=bar,
args=(a_server,)
).start()
高级:拓展至其他app/社交平台
目标:使用MetaPuppetForPython框架与web app通信 要点:MetaPuppetForPython将机器人本身作为服务器,将Wechaty作为客户,但其实可以有多个客户同时与机器人进行交互,可以是微博,QQ,或者网页应用等。 你可以继承
SweetSocketServer并overrideprocess_socket_message()和process_custom_message()以处理来自其他app的信息。
服务器:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import time
from MetaPuppet.core.SweetSocketServer import SweetSocketServer
from MetaPuppet.core.RobotBase import RobotBase
class ExtendedSocketServer(SweetSocketServer):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.webgui_room = 'webgui'
async def process_socket_message(self, sid, message, verbose=False):
sender = message['sender']
if sender.startswith('wx_'):
room_name = self.wx_room
elif sender.startswith('webgui_'):
room_name = self.webgui_room
else:
room_name = sender
text = message.get('text', '')
if text == 'CONNECTED':
print('{}: sender, sid, room_name'.format(text), sender, sid, room_name)
self.sio.enter_room(sid, room_name)
self.add_room(
sender=sender,
room_name=room_name,
)
else:
pass
async def process_custom_message(self, sid, message, verbose=False):
sender = message['sender']
msg_type = message.get('type', '')
if sender.startswith('webgui_'):
if msg_type == 'CHAT_INFO':
print('webgui info received', message)
await self.robot.process_webgui_chat_message(message, verbose=verbose)
pass
class MyBot(RobotBase):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
async def _process_message(self, message, verbose=False):
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
return_msg = None
if 'payload' in message and 'text' in message['payload']:
return_msg = message['payload']['text'][::-1]
return return_msg
async def _process_friend_invitation(self, message, verbose=False):
return_msg = {
'wx_msg_type': 'TEXT',
'path': 'Hello Human!',
}
return return_msg
async def process_webgui_chat_message(self, message, verbose=False):
return_msg = await self._process_webgui_chat_message(message, verbose=verbose)
return return_msg
async def _process_webgui_chat_message(self, message, verbose=False):
print('message', message)
return None
if __name__ == '__main__':
# init
a_bot = MyBot(name='test')
a_server = ExtendedSocketServer(
robot=a_bot,
num_async_threads=1,
debug_mode=True
)
a_server.run()
print(
'Please make sure the client is connected '
'before run the following codes'
)
time.sleep(20)
# -------------edit following code for simple tasks-----------------------
Web app作为客户端(示例中的任务不需要性能,可以直接用同步代码):
import socketio
import json
import os
class WebClient(object):
def __init__(self,
config_path):
self.config_path = config_path
self.config = self.read_config(config_path=self.config_path)
self.sio = socketio.Client()
self.create_response_functions()
def read_config(self, config_path):
# get config
with open(config_path, 'r') as fr:
config = json.load(fr)
return config
def run(self):
self.sio.connect('http://{}:{}'.format(
self.config['server']['host'],
self.config['server']['port'],
))
# use sio.wait if no other process keeping the program living
# self.sio.wait()
...
def create_response_functions(self):
@self.sio.on('message')
def process_msg_from_server(message):
...
@self.sio.on('connect')
def on_connect():
print('CONNECTED')
msg = {
'type': 'SOCKET_INFO',
'text': 'CONNECTED',
}
self.send_msg_to_server(msg)
@self.sio.on('disconnect')
def on_disconnect():
print('DISCONNECTED')
def send_msg_to_server(self, msg):
msg_to_send = {
'sender': 'webgui_client',
'status': 'NORMAL',
}
if isinstance(msg, str):
msg_to_send['text'] = msg
elif isinstance(msg, dict):
msg_to_send.update(msg)
else:
msg_to_send['status'] = 'ERROR'
self.sio.emit(
'message',
msg_to_send,
)
a_webgui = WebClient(
config_path=os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '../config.json')
)
# run is a dead loop if sio.wait() called, so we should call lastly
a_webgui.run()
原理
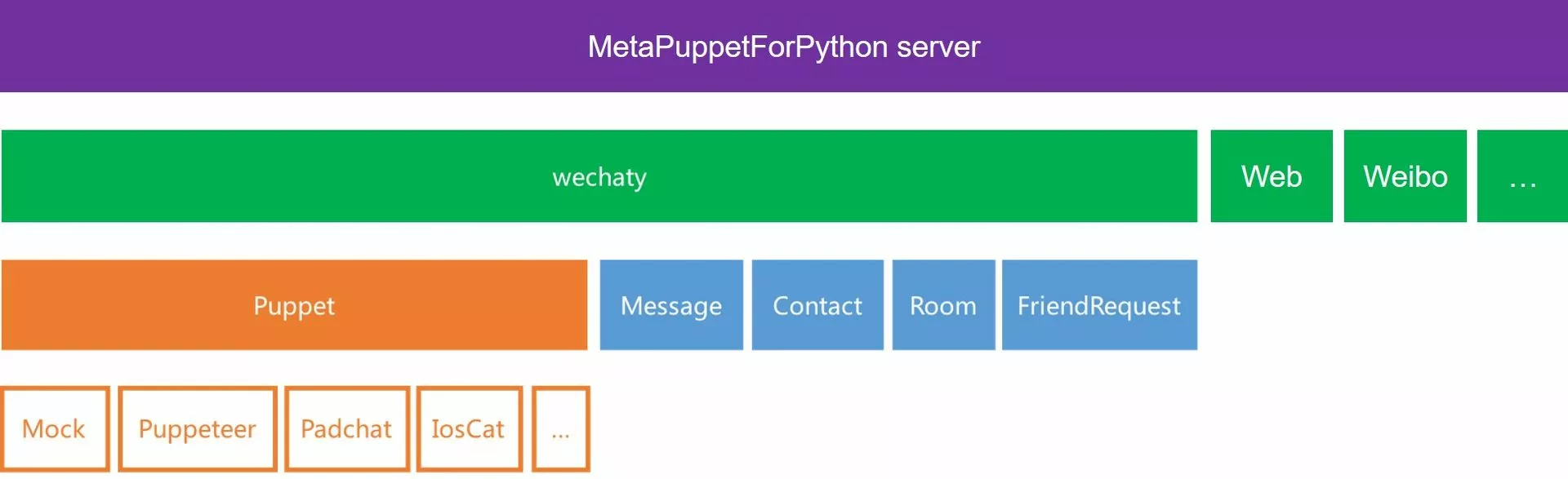
MetaPuppetForPython的核心是通过socket双向通信,实现业务逻辑(server)与第三方业务(client)的交互,包括信息的收发以及接口的调用等。
所以,在这个框架下,与Wechaty的架构类比,server是Wechaty的TS代码,client是Wechaty调用的各个puppet。
MetaPuppetForPython默认包括完全的server和运行Wechaty的client代码,针对其他app(weibo, qq, web, etc.)的client需要自定义。
对于想要一个python版本的Wechaty的童鞋来说,默认的代码已经够用。
针对Wechaty而言,server使用python-socketio,client使用socket.io-client,从而建立起双向异步通信。
主要的业务逻辑在server端,使用Python控制。
在需要调用Wechaty时,使用Python将文本形式的小段ts代码发送给client,client将其编译运行。
client端包含少量的ts代码,用于编译来自server的代码,和响应微信的请求(新消息,好友请求等),一般不需要更改。
基于此原理,可以使用Python调用Wechaty的任意原生代码,所以理论上可以兼容Wechaty的所有协议和接口函数。
已实现async_exec_wx_function()用于运行代码块,和async_exec_one_wx_function()用于运行单个函数。
安装
git clone https://github.com/quantumFlame/MetaPuppetForPython.git
cd MetaPuppetForPython
pip install .
cd socket_client
# install node.js
# https://github.com/nodesource/distributions/blob/master/README.md
# Using Ubuntu
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_13.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
npm install -g ts-node
npm install -g typescript
sudo apt-get install autoconf
sudo apt-get install libtool
npm install
# or
# rm -rf node_modules package-lock.json
# npm install wechaty@latest
# npm install wechaty-puppet-padplus@next
# npm install qrcode-terminal
# npm install socket.io-client
# npm install @types/socket.io-client
# npm install @types/node
# npm install other packages if needed...
运行
# start client in one terminal
cd socket_client
# (before you run, you need a wechaty token and
# create the config.json file following
# the example config.example.json)
ts-node src/wechaty_actions.ts
# start server in another terminal
python example/hello_word.py
Keys to remember
-
Extend
RobotBaseand modify_process_message()to reply to various wechat messages. -
Compile your management tasks as
async_foo()and call withrun_coroutine_in_new_thread(). -
If you don’t like async, you can also run the sync version functions in new thread (see more details in
example/hello_world.py).
作者: Tom 代码: MetaPuppetForPython 首发于博客: 用Python写Wechaty程序 文本协议: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 CN
