Wechaty Puppet
What is Wechaty Puppet
The term Puppet in Wechaty is an Abstract Class for implementing protocol plugins. The plugins are the components that help the Wechaty to control the IMs like WeChat.
The plugins are named PuppetXXX, like PuppetPuppeteer is using the google puppeteer to control the WeChat Web API via a chrome browser, PuppetPadLocal is using the Pad Protocol to connect with WeChat Server.
For better understanding of the Puppet below are some links listed down:
- Puppet Providers Directory: https://wechaty.js.org/docs/puppet-providers/
- Puppet Compatibility Table: https://wechaty.js.org/docs/puppet-services/compatibility/
- Puppet Development Guide: https://wechaty.js.org/docs/puppet-providers/diy
- Puppet Related Links: https://github.com/wechaty/wechaty-puppet/wiki/Links
- Puppet Documentation: https://wechaty.github.io/wechaty-puppet/typedoc/classes/puppet.html
Show me the code
For a deeper understanding of the Puppet in Wechaty, you can read its documentation from https://wechaty.github.io/wechaty-puppet/typedoc/classes/puppet.html and source code if you like at https://github.com/wechaty/wechaty-puppet/blob/main/src/puppet.ts Below is an architectural diagram of Wechaty Puppet.

Important Puppets
| Puppet Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PuppetPuppeteer | A web solution to connect WeChat, Wechaty init is implemented by web WeChat, which injects JavaScript code into chrome. |
| PuppetMock | A mock function to connect WeChat, not a real implementation, for testing other connectors to connect with Wechaty. This is used to further to connect other solutions, such as iPad, Xposed, iOS and windows client, |
| PuppetPadLocal | An iPad solution to connect WeChat. |
| PuppetService | It is a gRPC solution. |
Using Puppet with Wechaty Examples
-
Using wechaty-puppet-mock to run ding-dong-bot
WECHATY_PUPPET=wechaty-puppet-mock npm start -
Using wechaty-puppet-padpro to run ding-dong-bot
WECHATY_PUPPET=wechaty-puppet-padpro npm start
Basic Rules
Here are some rules that a Wechaty Puppet should follow:
- Emit Self Messages: when the bot says anything, the bot should receive a message said by itself. (and the
message.self()will return true for this message) - Perfect Logout:
logoutmethod should clean all the user session data from the puppet service, and the status of the App on the phone should display correctly (not log in on any devices). - State-less Session Management (with MemoryCard support): the puppet service should save the user session data to the memory card, and can be restored from the memory card.
- MIME File Name Extension Convention: FileBoxChunk.name must be able to convert to a MIME type and visa versa. The puppet needs to set the name with the right extension (.jpg, .pdf, etc) to the name of the file box. See, See
- Perfect Restart: the puppet should be able to restart at least 3 times in the unit tests, and do not leave any timer in the event loop after the testings. (i.e. this unit test)
MemoryCard
When a Wechaty bot is logged in, it will have a authorized secret data to store logged-in session, for example, the device information (62 data for pad protocol), the cookie (if you are using the web protocol), and the user session secrets, etc.
The memory card is a module designed to store those data.
Wechaty bot login with memory card module
- wechaty start()
- wechaty instanciates memory card (see wechaty.ts:start())
- wechaty set memory card to puppet (see wechaty.ts:initPuppet()) a. puppet start() b. puppet load session from memory card c. puppet logged in i. by loaded session, or ii. by scan qr code d. puppet save the session secret data to memory card
- memory card will be saved to file or network storage for future reuse.
By saving the user login session secret data to memory card, the Wechaty system can save the state to local, so that it can make the puppet service provider stateless. Currently neither of the Donut, WXWork, Rock, PadLocal have support for this stateless feature, nor the Wechaty system is ready for it.
Event Order
The order of events before the bot starts is very important and this section explains it in a a detailed manner:
- When you first start the bot, the
loginevent is first generated. - However, the Wechaty system needs to load the contact payload of the
userSelfbefore it emits theloginevent because the login event of Wechaty needs to take auserSelfinstance.So there will be some delay before the Wechaty emit theloginevent after it received theloginevent from its puppet. - Then the
ready-edevent is generated.The event is generated just before thereadyevent. - Then lastly the
readyevent is generated.
For a more robust Wechaty system, we can consider saving the ready event if the login event is not emitted in Wechaty and when we emit the login event in Wechaty, we can check if the puppet has already ready-ed, and if so, it can emit the ready event right after the login event.See
Event: ready
Need to fire ready event after the bot logined and all data has been synced.
For example, after we re-installed the WeChat app on our phone, it has to load contacts/rooms from the server for a long time. check
Payload Cache Management
- If the low-level puppet wants to dirty a payload, emit a
dirtyevent. The payload will be thetypeand theidof the paload - If the high-level puppet wants to dirty a payload, call
dirtyPayload(type, id)method, what it does (and only does) is to make the low-level puppet emit adirtyevent. - Each puppet should listen to the
dirtyevent, and callXXXPayloadDirty(id)to purge the internal cache of the specific payload inside itself Related issues:
- Specification for dirty event, dirtyPayload(), and `XXXPayloadDirty() to puppet abstraction, puppet implementation, puppet server, and puppet client. wechaty/wechaty-puppet-service#164
- No contactPayloadDirty method in puppet-implementation. wechaty/wechaty-puppet-service#43
- add dirty rpc function definition for sync data wechaty/grpc#79
Event: heartbeat
Puppet must emit heartbeats to provide a health check signal.
The heartbeat design
Here are the details:
- Wechaty Puppet is designed to emit at least one event in 60 seconds. If we do not have any events to emit, then we need to emit a
heartbeatevent so that it can prove itself as alive and healthy. See - It seems that the PadLocal does not have any
heartbeatevent to emit when there are no other events, so if your bot idle for more than 60 seconds, then the Wechaty Puppet system will think the puppet provider is dead, so it will callresetto try to recover the puppet.
A leaking of heartbeat example logs:
02:00:13 INFO StarterBot Message#Text[🗣Contact<OssChat>@👥Room<ChatOps - Heartbeat 💖>] [太阳]
02:01:13 WARN Puppet dogReset() reason: {"data":"onGrpcStreamEvent(EVENT_TYPE_MESSAGE)","timeout":60000}
02:01:13 VERB Puppet reset(onGrpcStreamEvent(EVENT_TYPE_MESSAGE))
02:01:13 VERB PuppetService stop()
02:01:13 VERB StateSwitch <PuppetService> off(pending) <- (false)
02:01:13 VERB PuppetService stopGrpcStream()
02:01:13 VERB PuppetService stopGrpcClient()
02:01:13 VERB Puppet selfId()
02:01:13 VERB StateSwitch <PuppetService> off(true) <- (pending)
02:01:13 INFO StarterBot Contact<Mike (李卓桓)> logout
02:01:13 VERB PuppetService start()
02:01:13 VERB StateSwitch <PuppetService> on(pending) <- (false)
02:01:13 VERB PuppetService startGrpcClient()
02:01:13 VERB PuppetService discoverServiceIp(e49007b7-7523-4a80-bfdb-1be0de3844b9)
02:01:14 VERB PuppetService startGrpcStream()
02:01:14 VERB StateSwitch <PuppetService> on(true) <- (pending)
02:01:14 VERB PuppetService onGrpcStreamEvent({type:EVENT_TYPE_LOGIN(25), payload:"{"contactId":"wxid_a8d806dzznm822"}"})
02:01:14 INFO StarterBot Contact<Mike (李卓桓)> login
02:01:15 VERB PuppetService onGrpcStreamEvent({type:EVENT_TYPE_READY(23), payload:"{"data":"ready"}"})
02:01:15 VERB StateSwitch <WechatyReady> on(true) <- (true)
02:01:20 VERB PuppetService onGrpcStreamEvent({type:EVENT_TYPE_READY(23), payload:"{"data":"ready"}"})
02:01:20 VERB StateSwitch <WechatyReady> on(true) <- (true)
heartbeat Example
Here's an example from our puppeteer puppet, which emits heartbeats in the browser, so if the browser dead, we will get to know because the heartbeat will be lost.Also check out the docs on Heartbeat Plugin.
Important Links
Please refer to the below links for more information on different methods of Message class:
Wechaty now support very limited Message types for more information check here In order to support receiving more message types, like audio, look here
Also note that Video type Message is not supported right now by Wechaty.
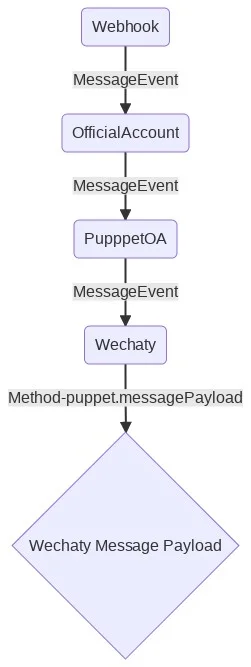
Wechaty Puppet Message Processing Flow
-
The Webhook gets called by the Tencent Server.
-
The message event will be propagated from the
Webhookclass to theOfficialAccountclass: -
The message event will be propagated from the
OfficialAccountclass to thePuppetOAclass: -
After message event be propagated from the PuppetOA to Wechaty, then the puppet.messagePayload() will be called to get the Wechaty Message Payload. Here is the most important part: we need to construct a Wechaty Message Payload from the Raw Message Payload (source code at here):
const rawPayload = await this.messageRawPayload(messageId)
const payload = await this.messageRawPayloadParser(rawPayload)
Future Enhancements
Futute enhancements can be to add more types of Message that Wechaty can support by implementing the messageRawPayload methods, which can be found here and also check out this link for more information.
Wechaty Puppet Uses
Ding/Dong Protocol
Ding dong protocol is a rule built using the Puppet which has a API named ding(data: string): void, and the Puppet has the following functionality:
- emit a
dongevent when theding()method has been called - the payload of the
dongevent might contains adatakey with the value exactly match thedatawhen calling theding()method.
For further information about the uses Ding dong protocol check out Ding Dong Bot
Learn More
- Puppet Related Links: https://github.com/wechaty/wechaty-puppet/wiki/Links
NPM publications
-
wechaty-puppetis not a dependency. It should be put in devDependencies and peerDependencies -
wechatyis not a dependency. It should be put in devDependencies and peerDependencies - must exist
examples/ding-dong-bot.tsto implement the ding/dong logic, use puppet API only.